Excessive sugar intake substantially undermines health by accelerating the aging process, impairing skin elasticity through the loss of collagen, and exacerbating metabolic disturbances. This dietary culprit contributes to a greater risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disorders. By understanding the impact of sugar and controlling its consumption, one can improve overall well-being and reduce these detrimental effects. Further exploration will reveal practical strategies to mitigate sugar's adverse influences on health.
Key Takeaways
- Sugar accelerates aging by damaging collagen through glycation, leading to wrinkles and saggy skin.
- Excessive sugar intake can decrease insulin sensitivity, heightening the risk of metabolic syndrome.
- High sugar consumption is linked to chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Hidden sugars in processed foods contribute to obesity and various health complications.
- Sugar addiction promotes compulsive eating behaviors, exacerbating health risks and chronic inflammation.
Accelerating the Aging Process: Sugar's Impact on Skin and Body
Accelerating the aging process, sugar has a profound impact on both skin health and overall bodily function.
When sugar is metabolized, it binds with proteins in a process known as glycation, leading to the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs).
These AGEs play an essential role in the depletion of collagen, a protein critical for maintaining skin elasticity and strength.
As collagen diminishes, the skin begins to show signs of aging, such as wrinkles and sagging.
In addition, disrupted sugar metabolism can exacerbate these effects, accelerating the visible signs of aging and impacting the body's overall well-being.
The Hidden Dangers of Excessive Sugar Consumption
While the impact of sugar on aging is well-documented, its broader implications on health are equally significant. Excessive sugar consumption harbors hidden dangers, often masked in processed foods as hidden sugars.
These stealthy additives contribute to various health issues beyond the obvious risk of obesity. Increased sugar awareness is vital as many consumers unknowingly ingest large quantities of sugar, elevating their risk for chronic diseases.
Educating the public about these hidden sugars and promoting label transparency can empower individuals to make healthier choices, potentially reducing the prevalence of sugar-related health complications and enhancing overall well-being.
How Sugar Affects Your Metabolic Health

Despite its widespread consumption, sugar has profound negative effects on metabolic health, often contributing to serious conditions such as metabolic syndrome. Excessive intake of sugar can lead to decreased insulin sensitivity, a key factor in the development of metabolic syndrome. This condition encompasses a cluster of symptoms including increased blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Understanding and moderating sugar intake is essential for maintaining metabolic health.
| Impact on Health | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Reduced Insulin Sensitivity | Higher risk of metabolic syndrome |
| Increased Blood Sugar | Potential for type 2 diabetes |
| Abnormal Cholesterol Levels | Increased cardiovascular risk |
| Excess Body Fat | Elevated blood pressure |
| Overall Metabolic Stress | Compromised physical and mental health |
The Link Between Sugar Intake and Chronic Diseases
Given the extensive evidence, it is clear that high sugar intake is closely linked to the development of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
Sugar addiction and the resulting chronic inflammation play pivotal roles in this process.
Consider the following:
- Sugar Addiction: Fuels compulsive eating behaviors, increasing risk factors for disease.
- Chronic Inflammation: Triggered by excess sugar, contributes to tissue damage and various chronic conditions.
- Type 2 Diabetes: High sugar diets can lead to insulin resistance.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Linked to high sugar intake through adverse lipid profiles.
- Obesity: Sugar-laden diets contribute greatly to excessive calorie intake and weight gain.
Sugar's Role in Skin Damage and Premature Aging
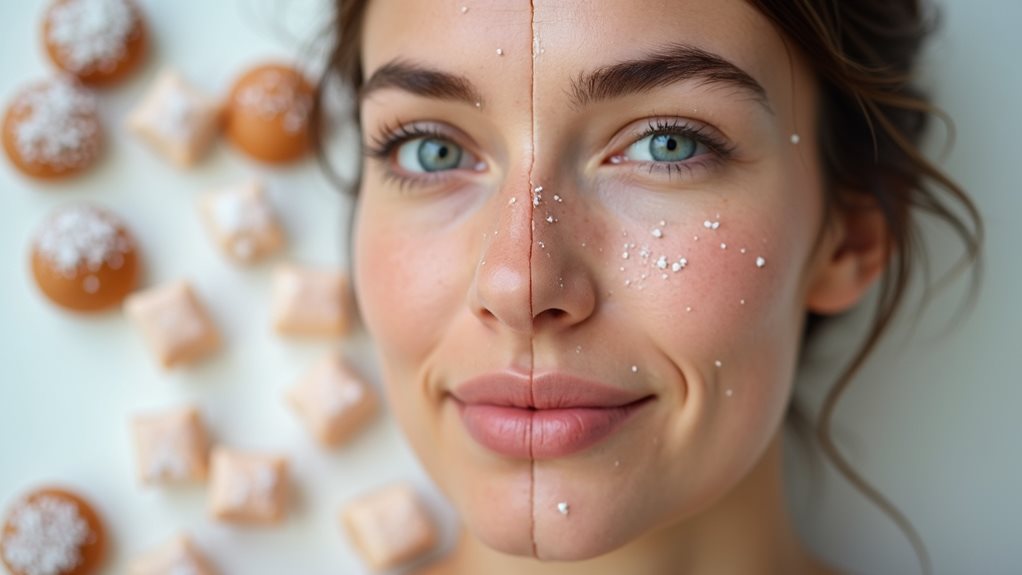

The detrimental impact of sugar on skin health and the acceleration of premature aging are increasingly recognized in scientific research.
When sugar is consumed in excess, it undergoes a process known as glycation, where sugar molecules attach to proteins, including collagen. This interaction leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which greatly impair collagen's structural integrity and function.
Collagen depletion due to sugar glycation not only reduces skin elasticity but also enhances wrinkle formation. The cumulative effect manifests as visible signs of aging, underscoring the importance of moderating sugar intake to maintain skin health and well-being.
Strategies to Combat Sugar Cravings and Improve Your Diet
Understanding the harmful effects of sugar on skin health and aging underscores the importance of managing sugar cravings and improving dietary habits.
Implementing specific strategies can greatly enhance overall well-being:
- Incorporate sugar substitutes like stevia or erythritol to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing sweetness.
- Practice mindful eating to increase awareness of hunger cues and reduce impulse snacking.
- Choose fiber-rich foods which help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Drink plenty of water, often thirst is confused with sugar cravings.
- Engage in regular physical activity to boost mood and reduce the urge for sugary treats.
These methods foster healthier dietary choices and manage cravings effectively.
The Benefits of Reducing Sugar in Your Daily Life

Reducing sugar intake greatly enhances overall health and well-being. By opting for sugar alternatives and engaging in mindful eating, individuals can mitigate risks associated with high sugar consumption.
These practices help prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular complications. Additionally, less sugar promotes better mental clarity and energy stability, avoiding the typical highs and crashes associated with sugary diets.
Embracing sugar alternatives not only supports physical health but also encourages a more attentive relationship with food, leading to improved dietary choices.
Ultimately, reducing sugar intake contributes to a healthier lifestyle and long-term well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Sugar Intake Affect Children Differently Than Adults?
Sugar intake affects children differently than adults by potentially altering their metabolism and increasing the risk of childhood obesity, necessitating careful monitoring of sugar consumption to safeguard against these long-term health implications.
Can Natural Sugars Cause the Same Damage as Processed Sugars?
Natural sugars, though cloaked in the guise of health, can release havoc similar to processed sugars, contributing to aging, weight gain, and metabolic disturbances when consumed in excess. Moderation remains key to mitigating damage.
Are Sugar Substitutes Safer or Healthier Than Actual Sugar?
The current question explores whether sugar substitutes offer safer or healthier alternatives to sugar. Evidence suggests that while substitutes may reduce calorie intake, their long-term health benefits and safety remain subjects of ongoing research.
What Role Does Genetics Play in Sugar Addiction and Its Effects?
Like a key fitting a lock, genetic predisposition can influence one's susceptibility to sugar cravings. Research suggests that genetics play a significant role in sugar addiction and its consequential health effects.
How Can I Accurately Track My Daily Sugar Intake?
To accurately track daily sugar intake, one can utilize tracking apps that log food consumption and read sugar labels on products to monitor intake. This method guarantees a precise and informed approach to dietary management.
Conclusion
In summary, while sugar provides immediate energy, its excessive consumption is linked to numerous health concerns. For example, studies show a 25% increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes with high sugar diets. Reducing sugar intake can slow aging, improve metabolic health, and decrease the likelihood of chronic diseases. Adopting mindful eating practices and healthier lifestyle choices are essential in mitigating these adverse effects, underscoring the importance of moderation for long-term well-being.